Mushrooms are the fruiting bodies of fungi. Mycelial hyphae form webs underground that stretch up to thousands of acres in branches of tube like cells. Their growth patterns resemble those of neurons.
Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system. They are responsible for receiving sensory input, transmitting signals, and enabling communication throughout the body.
Everything in the universe is connected through patterns of information encoded by chemical messages. Everything we as humans experience involves some kind of neurochemical interaction.
Indigenous cultures consumed hallucinogenic indolamines for thousands of years as medicines.
The Human Nervous System
Our nervous system is a complex network responsible for receiving, processing, and responding to information, enabling communication and coordination within the body

The nervous system of the forest
Mushrooms act as environmental ‘sensors’, constantly navigating their surroundings through their underground communication with trees, plants, and soil microorganisms.
They negotiate nutrients and resources, communicate environmental threats like drought and insect infestation, and use sensory information to solve problems and make decisions.
They achieve this using electrical activity and neurotransmitters that are startlingly similar to those in the human brain and gut, which some scientists describe as intelligent communication.
Adamatzky A. Language of fungi derived from their electrical spking activity. R Soc Open Sci. 2022;9(4):211926.
Bio-Chemicals of Magic Mushrooms
Among the millions of identified fungal species, approximately two hundred produce psychedelics. Psilocybin, the psychoactive component of magic mushrooms.
Some plants produce N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), which is considered an archetype hallucinogen. This is because its basic chemical structure is repeated across other common psychedelics, including psilocybin.
Humans and other animals also produce endogenous (originating within an organism or part of an organism) psychedelics. Some of these are identical or closely resemble those produced by fungi and plants.
Compounds like serotonin and melatonin found in fungi, plants, animals, and humans are all basically the same.
Indolamines
Indolamines are a family of neurotransmitters that share a common molecular structure to neurotransmitters like serotonin and melatonin. These play crucial roles in mood, sleep, and other biological processes.

Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is a well-known indolamine that signals between the gut and brain to coordinate digestion, appetite, mood, learning, memory, cognition, blood vessel constriction, and sleep.
The human gut produces more than 90 percent of the body’s serotonin with the help of resident microbes.
The natural function of endogenous hallucinogens might be to protect neurons from hypoxia which occurs when oxygen is insufficient at the tissue level to maintain adequate homeostasis.
The beneficial effects of psychedelic therapy are mediated through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, the two-way communication between the gut’s nervous system, also known as the enteric nervous system, and the brain.
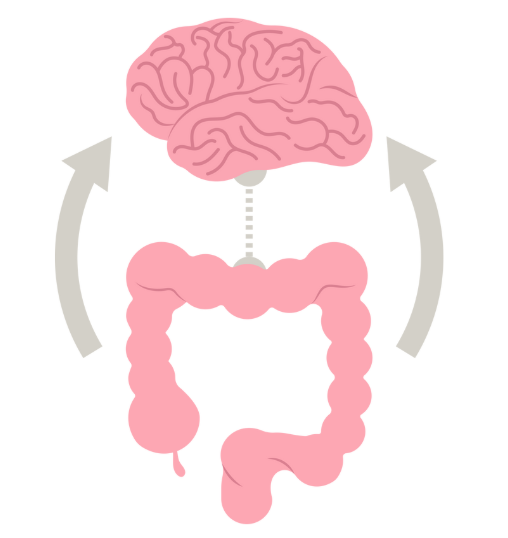
If someone were to suffer a physical trauma, lose blood, and go into a hypoxic state, endogenous hallucinogens would help neurons survive.
There is also growing evidence to support that Psychedelics improve depressive symptoms, create Neuroplasticity and overall happiness.